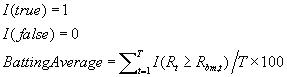Rt = return of subject for time period t
Rbm,t = return of benchmark for time period t
T = number of time periods
n = number of time periods in a year (12 if monthly returns are used)
Let I be the indicator function such that
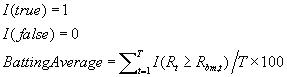
Batting Average is a measure of a manager's ability to consistently beat the market. It is calculated by dividing the number of months in which the manager beat or matched an index by the total number of months in the period. For example, a manager who meets or outperforms the market every month in a given period would have a batting average of 100. A manager who beats the market half of the time would have a batting average of 50.
Rt = return of subject for time period t
Rbm,t = return of benchmark for time period t
T = number of time periods
n = number of time periods in a year (12 if monthly returns are used)
Let I be the indicator function such that